Publication date:
Dec 11, 2025
IMF Data Brief: Financial Soundness Indicators
Notable Cross-Country Variation in Non-Bank Financial Institutions’ Balance Sheets Point to Diverging Risks
Financial Soundness Indicators, Country data, Quarterly
Contributors: Hector Carcel Villanova, Abdulrahman Gweder, Mahmut Kutlukaya, Miguel Segoviano, Ibrahim Serwanja
The growing share of non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) in the financial sector underscores the importance of assessing potential risks associated with them. The IMF’s Financial Soundness Indicators (FSI) highlight notable cross-country differences in the balance sheet structures of NBFIs and shed light on different risks across institutions and countries.
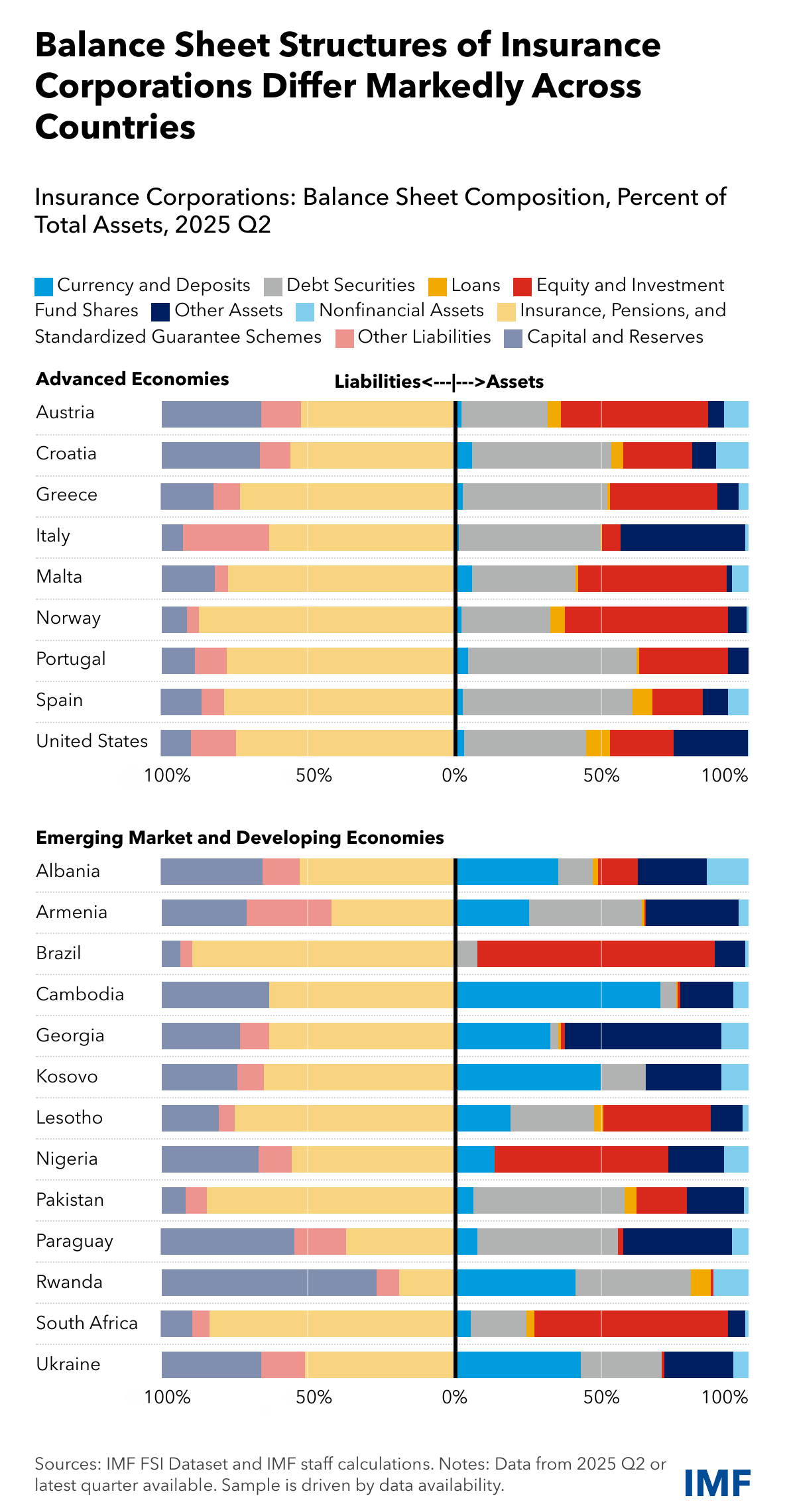
Insurance Corporations (ICs) in reporting advanced economies generally have balance sheet structures that differ markedly from those in reporting emerging market and developing economies. In the latter, they tend to maintain a higher share of capital and reserves on the liabilities side, while holding more currency and deposits among their assets. In advanced economies, they predominantly allocate their portfolios to debt securities and equity and investment fund shares.
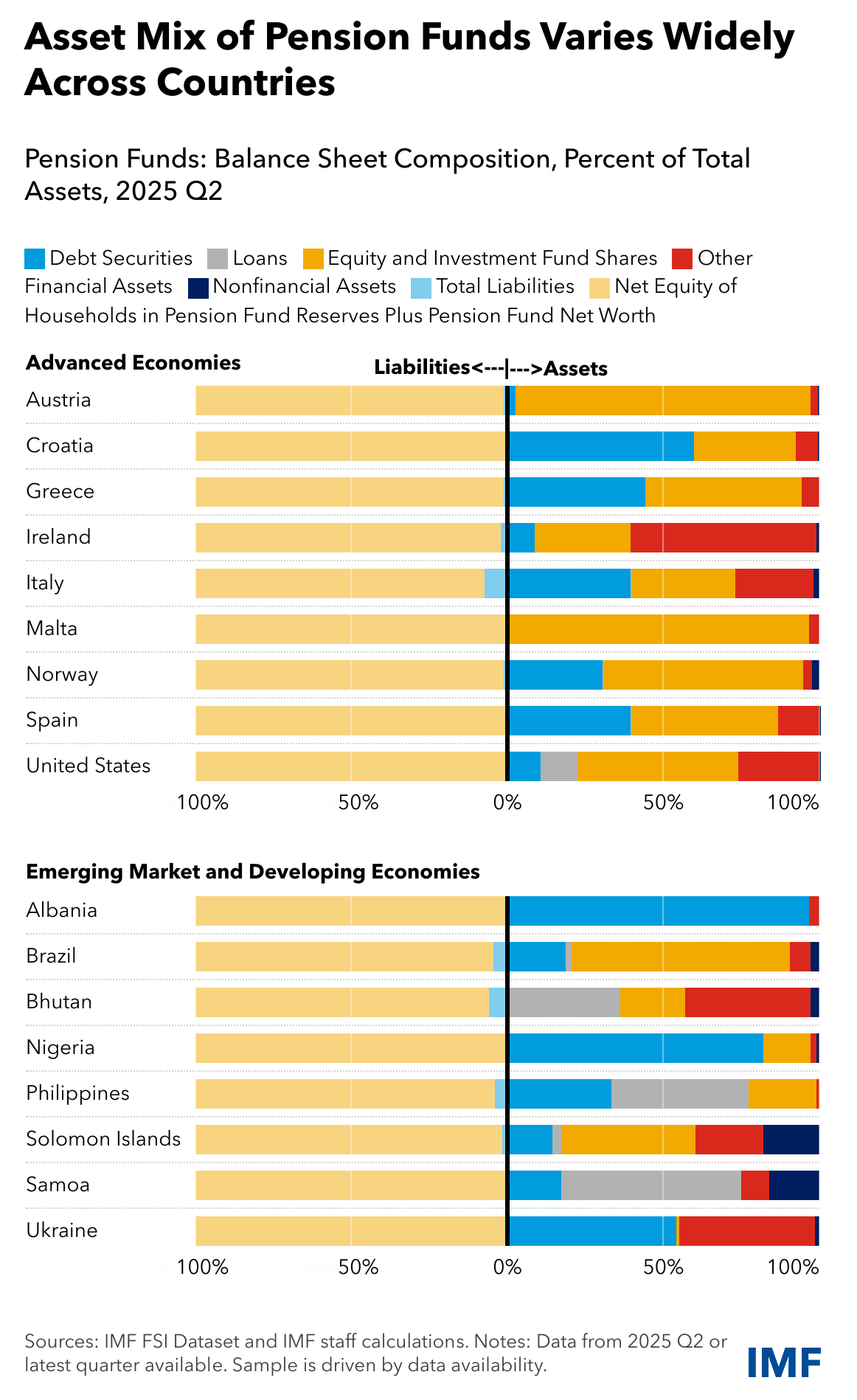
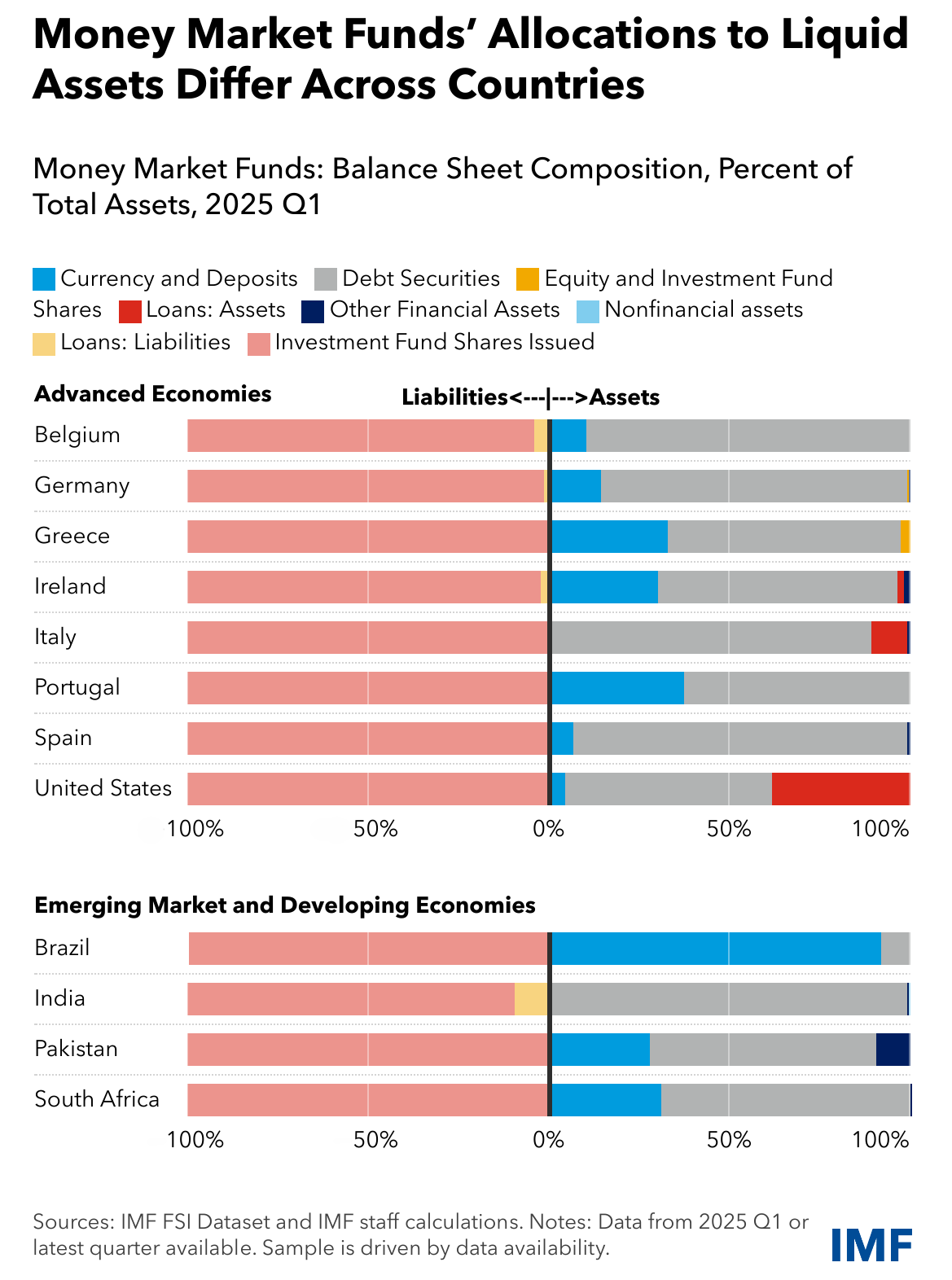
Pension Funds (PFs) and Money Market Funds (MMFs) exhibit marked differences in asset composition across countries, despite relatively similar liability structures. The asset mix of PFs varies widely across countries—in some countries, portfolios are heavily concentrated in equities, in others they are dominated by debt securities. In general, the net equity of households in the pension fund reserves remains the main funding source of PFs. MMFs rely on issuing investment fund shares for funding, but their asset portfolios differ in the proportions allocated to liquid instruments such as debt securities and currency and deposits.
Differences in NBFIs’ balance sheet structures expose them to different risks, implying that global or domestic shocks can propagate asymmetrically across financial systems. This highlights the critical value of NBFIs data for financial system surveillance to safeguard financial stability.
EMPOWERING THE WORLD WITH DATA
IMF Data is known for its high standard of quality and methodological consistency. With over 50 datasets updated regularly, you always have access to the latest global economic trends and forecasts as well as trusted data for cross country research and analysis.
Check our release calendar for upcoming releases:

